Understanding Heat Pumps: A Smart Choice for Sustainable Home Heating and Cooling
As the demand for greener, more energy-efficient home heating solutions grows, heat pumps have become a popular alternative to traditional boilers. Not only do they reduce your carbon footprint, but they also offer the dual benefit of heating and cooling your home—all in one system.
Types of Heat Pumps: Air Source vs Ground Source
1. Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHP)
Air source heat pumps absorb heat from the outside air and transfer it into your home. The process begins with drawing heat into a fluid refrigerant, which is then compressed to increase its temperature. This heat is used to warm your central heating system—via radiators or underfloor heating—and to heat water stored in a hot water cylinder for taps, showers, and baths. Air Source Heat Pump (ASHP) Diagram
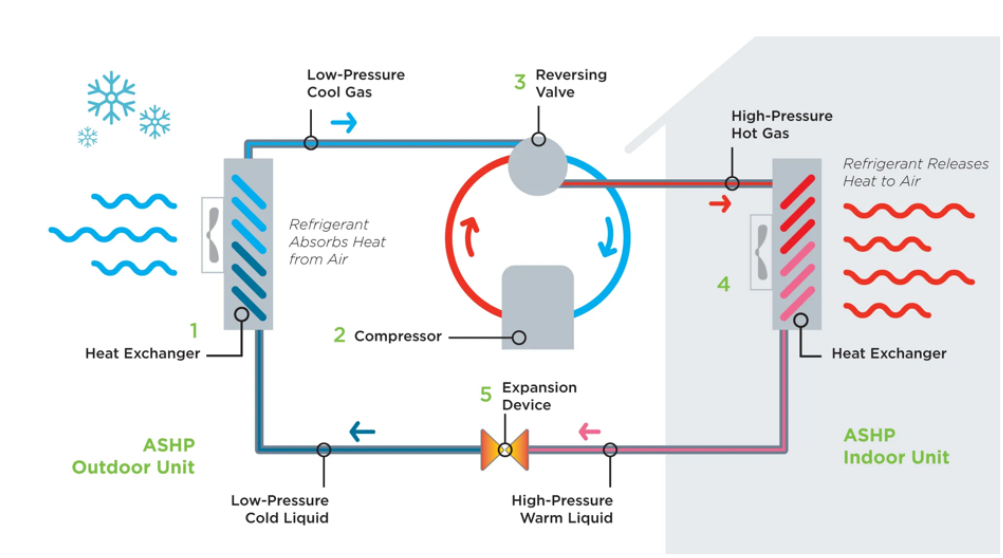
How it works:
1-Outdoor Heat Exchanger-Absorbs heat from the outside air. The refrigerant inside
the coil collects this thermal energy, even in low outdoor temperatures.
.
2-Compressor - Compresses the refrigerant gas, significantly raising its temperature
and pressure.
3-Reversing Valve - Directs the flow of refrigerant based on whether heating or
cooling is needed.
4-Indoor Heat Exchanger - Directs the flow of refrigerant based on whether heating or
cooling is needed.
5-Expansion Device - Lowers the pressure of the refrigerant so it can absorb heat again
from the outside air, repeating the cycle.
• Suitability: Ideal for most UK homes
• Installation Cost: Around £14,000 on average
- With the Boiler Upgrade Scheme, homeowners in England and Wales can
receive £7,500 towards installation
• Cost Influences:
- Heat pump size
- Property size
- Whether it’s a new build or retrofit
- Radiator upgrades
🌍 Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHP)
Ground source heat pumps extract heat from the ground using buried pipes filled with a thermal transfer fluid (a mix of water and antifreeze, often called "brine"). This fluid absorbs heat from the earth and passes it through a heat exchanger and compressor before heating your home and water. Ground Source Heat Pump Diagram
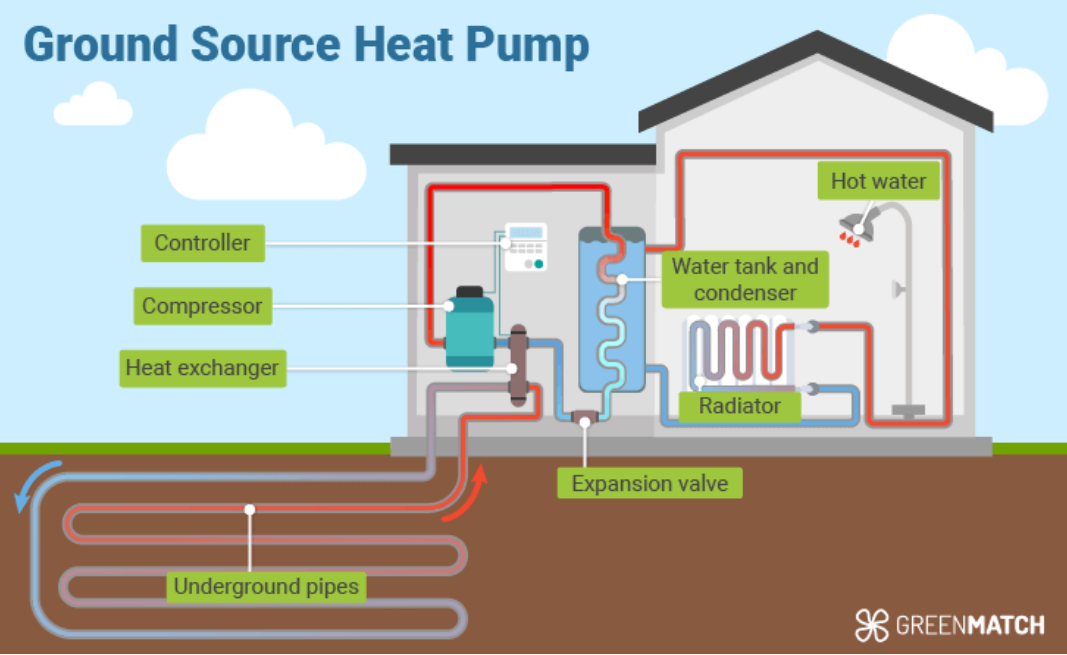
How it works:
Ground Loop:-Collects heat from the soil
.
2-Heat Exchanger: - Transfers ground heat to refrigerant
3-Compressor: - Increases refrigerant temperature
4-Heat Distribution System: - Delivers warmth into the home
• Installation Cost: Typically around £28,000 with trenches; more if using boreholes
• Installation Cost: Around £14,000 on average
• Cost Influences:
- Ground access and trench vs borehole
- Heat pump brand, model, and size
- Home size and heating demand
- Radiator or underfloor heating installations
- New build vs existing property
Benefits of Heat Pumps
-Lower energy bills over time
Reduced energy use: Heat pumps are over three to four times more efficient than
gas or oil boilers
Smaller carbon footprint: They use electricity—not fossil fuels—making them a
more sustainable option
While electricity prices are currently about four times higher than gas, heat pumps make up for this through their 300–400% efficiency, significantly reducing overall energy consumption.
- 📉 A 2023 study by CoreLogic found that households with heat pumps save on average £278 per year on energy bills.
- 💡 With smart tariffs (e.g., Octopus Energy’s “Cosy Octopus”), households can achieve up to 20% savings on electricity usage compared to standard rates.
Although heat pumps may currently cost slightly more to run than new gas boilers, long- term savings are expected to increase as electricity prices stabilize and the grid becomes greener.
2. Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHP):
Due to stable underground temperatures, GSHPs offer even greater long-term efficiency— especially in well-insulated homes. Running costs vary based on:
- System design
- Control settings
- Your electricity tariff
Final Thoughts
Heat pumps are a future-ready heating solution, offering impressive energy efficiency and the bonus of cooling in summer. With government grants, reduced energy usage, and the ability to cut carbon emissions, heat pumps represent a smart and sustainable investment for modern homes. If you're building or upgrading your home, integrating a heat pump could be the key to unlocking lower bills, a lighter footprint, and a healthier, more intelligent living space.